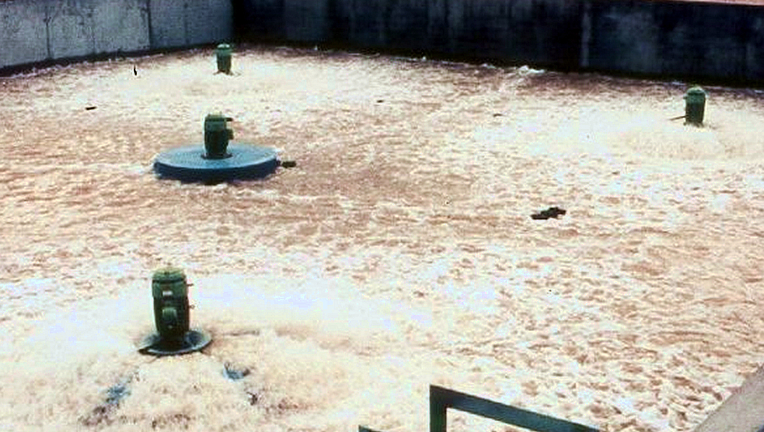
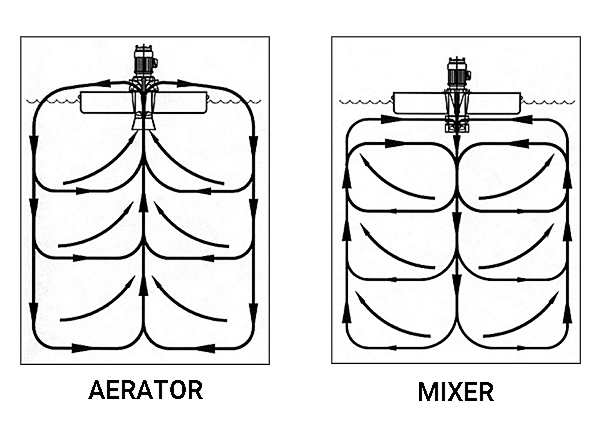
The floating aerators use their high pumping capacity to break up the surface wastewater into particles and spray it towards the bottom of the pond. By doing so, they create a larger surface contact area, thereby enhancing the transfer of oxygen to the wastewater. Furthermore, the aerators simultaneously disperse and mix this newly oxygen-enriched water. Ultimately, this comprehensive process effectively treats the wastewater.
Among the most common applications of the floating aerator are:
- Aerated lagoons,
- Stabilization ponds
- Sequential batch reactors SBRs,
- Oxidation Ditches
- Activated sludge,
- Aerobic digestion
- Improvements to existing systems
Benefits
- Failure-Free Performance
- Ease of Maintenance
- Low Maintenance Costs
- Tough in Extreme Conditions
Parts of Wastewater Floating Aerators
- Motor. The motor of a floating aerator shall have important design features. It shall endure a harsh, humid environment. It shall be Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled TEFC, with a Service Factor of at least 1.15. The fan shall be protected with a heavy-duty cover. It should be dynamically balanced and vibration tested at the factory. Additionally, it shall be energy-efficient. Motor speeds available are: 900, 1200, and 1800 rpm.
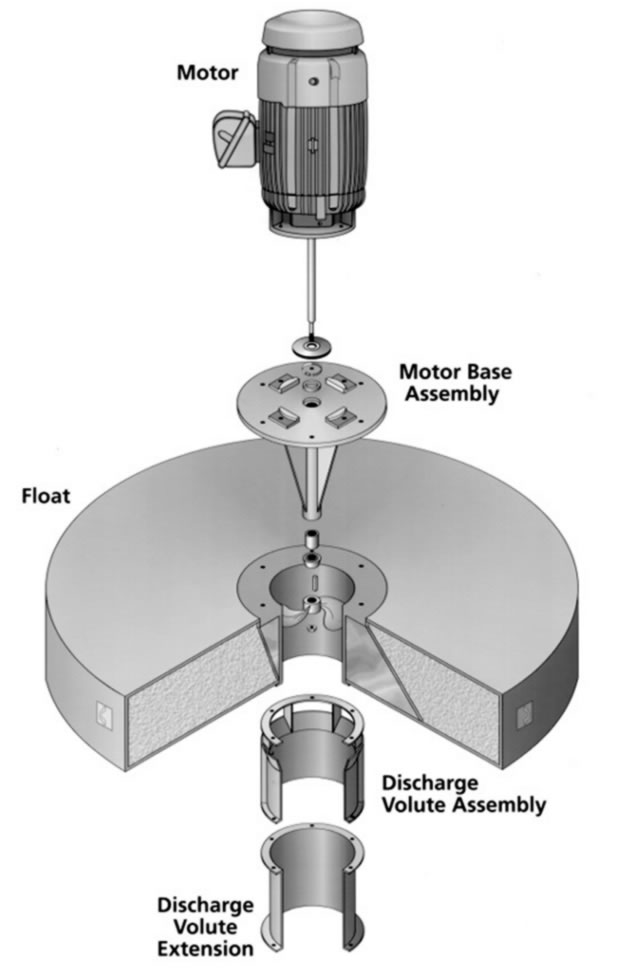
- Float. The float’s design provides maximum stability and buoyancy. Its exterior shell consists of either fiberglass (FRP) or stainless steel (SS). Closed-cell polyurethane foam fills the float, adding structural stability and preventing it from sinking if the exterior shell sustains damage.
- Motor Base Assembly.
- Shaft and Propeller.
- Discharge Volute
Flow Patterns of Surface Aerators and Mixers